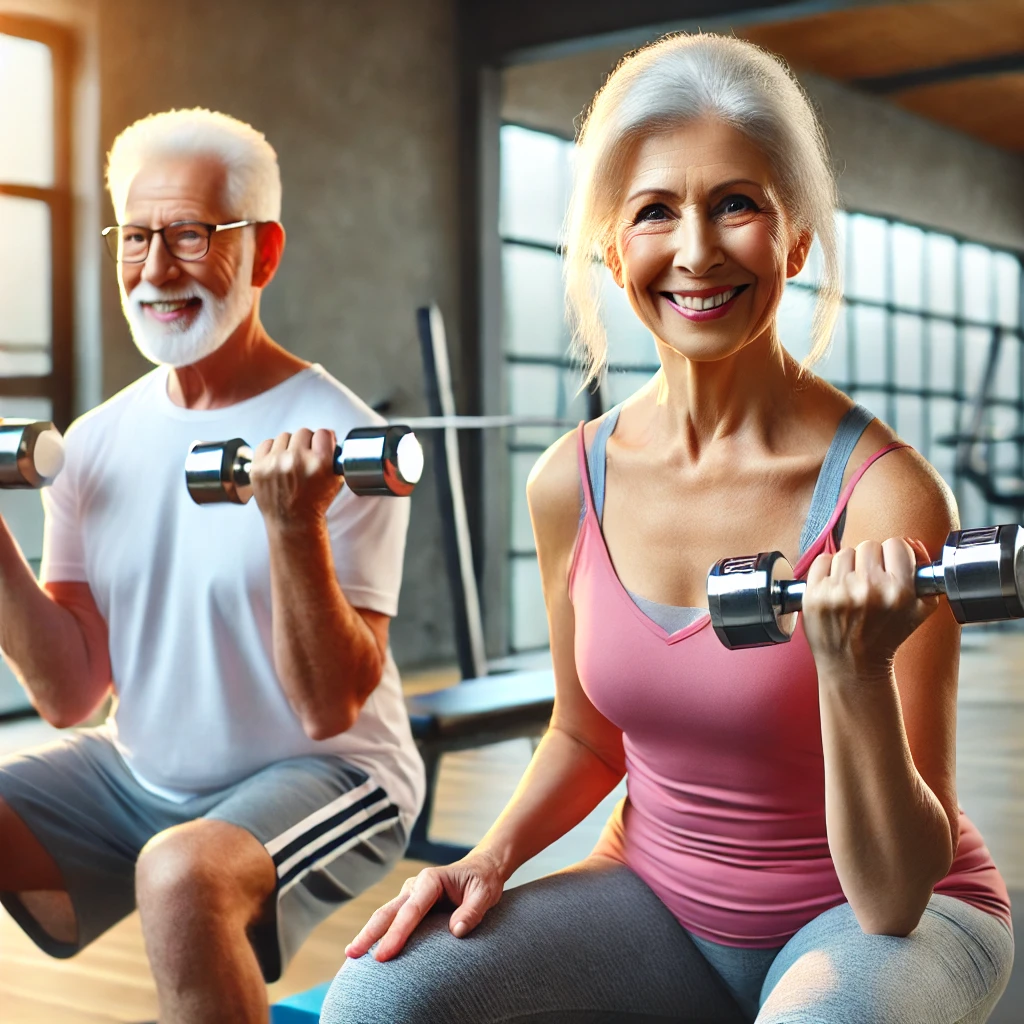
As we age, maintaining strength and mobility becomes crucial for a high-quality life. Strength training isn’t just for young athletes, it’s a powerful tool for seniors to stay independent, reduce health risks, and enhance overall well-being. Here’s why incorporating strength training into your routine can be a game changer in your golden years.
Understanding Strength Training for Seniors
Strength training involves exercises designed to improve muscle strength, endurance, and flexibility. These exercises may include resistance training with weights, resistance bands, bodyweight exercises, and even yoga. Unlike high-impact workouts, strength training is adaptable to various fitness levels, making it an excellent choice for seniors.
1. Preserves Muscle Mass and Strength
Aging naturally leads to muscle loss (sarcopenia), making daily activities like walking, climbing stairs, and carrying groceries more challenging. Strength training helps counteract this process by maintaining and even building muscle mass, allowing seniors to stay active and independent.
Example: Try bodyweight squats or chair squats to build lower body strength without strain.
2. Improves Bone Health
As bone density decreases with age, the risk of osteoporosis and fractures increases. Strength training stimulates bone growth by placing stress on bones, prompting them to strengthen. Weight-bearing exercises like squats, lunges, and resistance band training significantly improve bone health, reducing the likelihood of fractures and improving overall skeletal integrity.
Example: Perform resistance band leg presses to strengthen bones and muscles safely.
3. Enhances Joint Health and Reduces Arthritis Symptoms
Joint pain and stiffness can limit mobility and reduce overall quality of life. Strength training supports joint stability and flexibility, which can alleviate pain and stiffness caused by arthritis. Strengthening the muscles surrounding the joints reduces strain on them, leading to improved mobility and reduced discomfort.
Example: Seated knee extensions using light ankle weights can help with joint stability and movement.
4. Boosts Metabolism and Aids in Weight Management
As people age, their metabolism slows down, leading to potential weight gain and associated health risks. Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat, even at rest. Strength training helps maintain a healthy weight by boosting metabolism, reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and high blood pressure.
Example: Use light dumbbells for bicep curls to build muscle and promote calorie burn.
5. Improves Balance and Reduces Fall Risk
Falls are a leading cause of injury among seniors, often resulting in fractures and decreased mobility. Strength training improves core stability, coordination, and balance, reducing the likelihood of falls. Exercises such as leg lifts, seated leg extensions, and stability ball exercises help strengthen key muscle groups needed for balance and coordination.
Example: Stand on one leg for a few seconds while holding onto a stable surface to improve balance.
6. Supports Heart Health
Cardiovascular diseases remain a major health concern for older adults. Regular strength training lowers blood pressure, improves circulation, and enhances cardiovascular function. Combined with aerobic exercise, strength training contributes to a stronger heart and reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.
Example: Perform wall push-ups to enhance upper body strength while promoting cardiovascular health.
7. Enhances Mental Health and Cognitive Function
Strength training not only benefits the body but also has profound effects on the brain. Exercise releases endorphins, which reduce stress and anxiety while improving mood. Furthermore, research has shown that strength training is linked to enhanced cognitive function, improved memory, and a lower risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Example: Engage in light resistance band exercises while listening to music or a podcast to keep the brain engaged.
8. Increases Energy Levels and Reduces Fatigue
Engaging in strength training leads to better oxygen circulation, increased endurance, and higher energy production in the body. This results in greater vitality and reduced fatigue, enabling seniors to enjoy daily activities with more enthusiasm and less strain.
Example: Perform seated shoulder presses using light dumbbells to increase endurance and strength.
9. Encourages Social Interaction
Physical activity fosters a sense of community and connection. Whether joining a group exercise class, attending a senior fitness program, or working with a personal trainer, strength training offers opportunities for socialization. Exercising with peers promotes motivation, reduces feelings of isolation, and enhances emotional well-being.
Example: Participate in a local strength training class or virtual fitness group for motivation and support.
10. Enhances Overall Quality of Life
By improving physical strength, balance, and mental well-being, strength training enables seniors to maintain independence, enjoy hobbies, travel, and engage in daily activities without limitations. The ability to move confidently and perform daily tasks effortlessly contributes to a higher quality of life.
Example: Practice a combination of chair yoga and resistance band exercises to enhance flexibility and mobility.
Getting Started with Strength Training
Seniors interested in strength training should begin with simple, low-impact exercises and gradually progress to more challenging routines. Consulting with a healthcare professional or certified trainer ensures exercises are safe and appropriate for individual fitness levels. Key tips for starting a strength training routine include:
- Begin with light resistance: Use light dumbbells, resistance bands, or even bodyweight exercises.
- Focus on proper form: Performing exercises correctly prevents injuries and maximizes effectiveness.
- Incorporate variety: Combine strength training with flexibility and balance exercises for a well-rounded routine.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body responds and adjust intensity accordingly.
- Stay consistent: Aim for at least two to three strength training sessions per week for optimal results.
Conclusion
Strength training is a game changer for seniors, providing a pathway to a healthier, more active, and independent life. Whether through bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, or light weights, incorporating strength training into a routine can lead to profound benefits. The physical, mental, and social advantages of strength training make it an invaluable addition to any senior’s lifestyle. It’s never too late to start—stay strong, live long, and embrace the power of movement!